The Latino population in the United States has grown exponentially in the last decade. Being the 18.5% of the residents with a total of 60.6 million Hispanic citizens, therefore, making them the most significant minority in terms of economic growth and workforce representation, with 16.7% of the workforce.
As a result of different migratory circumstances and the lack of access to health care, the Latino Population is facing chronic conditions. Their consequences are affecting their families and the overall well-being of their communities.
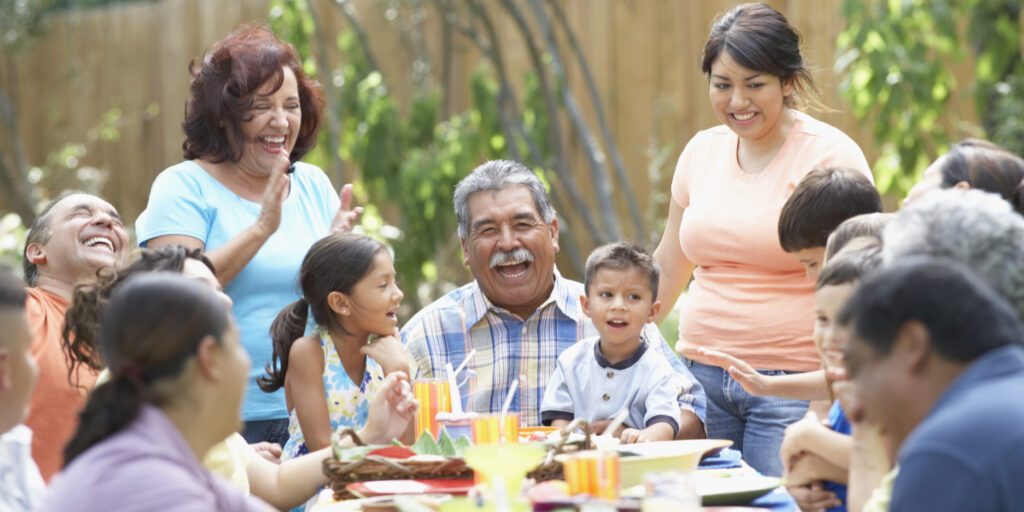

Currently, the Latino Population is 50% more likely to die from diabetes and liver disease than other populations. Where is also shown that heart diseases and cancer in Hispanics are the two leading causes of death among the population.
The UCLA Center for Health Policy Research Foundation estimates that about three-quarters of Latino children aged 18 and under are uninsured. According to the researchers, these children probably don’t visit the doctor regularly or receive routine examinations.
With the growing Latino population, healthcare and population management needs also rise. thus, making it necessary for most areas in the country to provide high-quality medical care to address disparities in health among them.
What are the current challenges in the Latino Population's healthcare system?
- A shortage of Spanish-speaking healthcare providers, on account of less than 8% of the workforce in rural areas.
- Migratory lifestyles lead to poor adherence to preventive and chronic condition management programs.
- Lack of transportation.
- Linguistic and cultural differences between healthcare professionals and medical staff.
- Unfamiliarity with local and rural healthcare services and how to access them.
- Low health literacy and lack of information.
- Limited availability of public health insurance.
How to address the Latino Population?
- Provide health care providers and medical staff with bilingual tools to help patients and their families. for example, interpreters and medical literature with easy access to their language.
Use of software and platforms that are tailored to fit health disparities for the Latino population.
Additionally, impart culturally concordant undergraduate and medical programs. This way, students can acquire medical knowledge while interacting with patients, doctors, preceptors, and medical interpreters.
About Esvyda
Esvyda
is the complete solution for patients in Latino Communities, where we present
software for telehealth, remote patient monitoring, BHI management, and digital
therapeutics.
Reference: Oh, H. et al. (2020) “Addressing barriers to primary care access for Latinos in the U.S.: An agent-based model,” Journal of the Society for Social Work and Research, 11(2), pp. 165–184. Available at: https://www.journals.uchicago.edu/doi/full/10.1086/708616